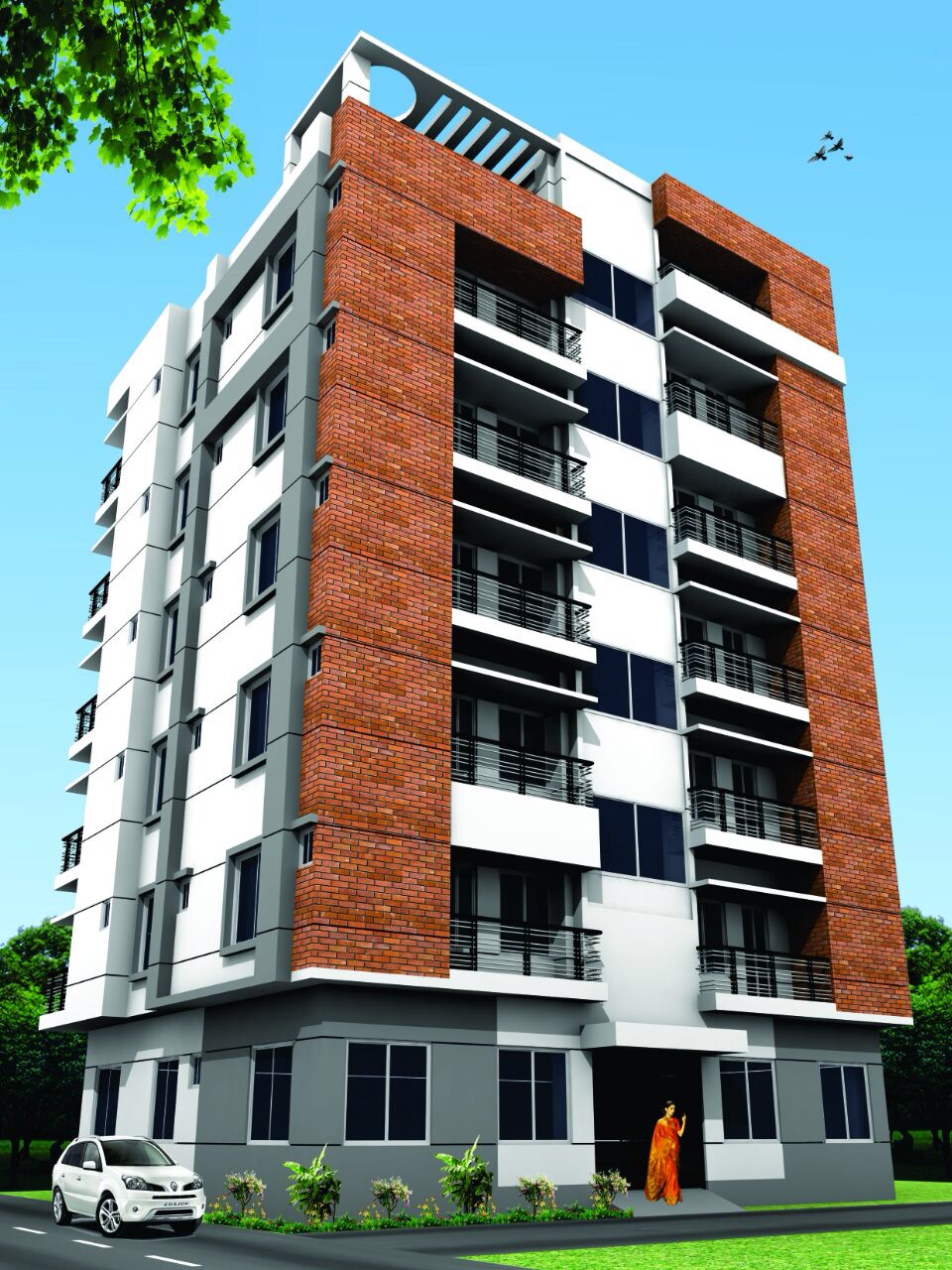

In the Information and communication era our main concern is that to develop the community concerning the global village. Dynamic Architects & Engineers manages the complete architectural solution for clients such as architectural design, estimating, construction and plumbing. We try to contribute to GDP by providing real estate-related services for the nation.
Some of our valuable clients are shown below.

It's important to note that architects often collaborate with other professionals, including structural engineers, landscape architects, and interior designers, to ensure a comprehensive and well-coordinated approach to the design and construction process. Architecture services can vary widely based on the specific needs of the client and the nature of the project.
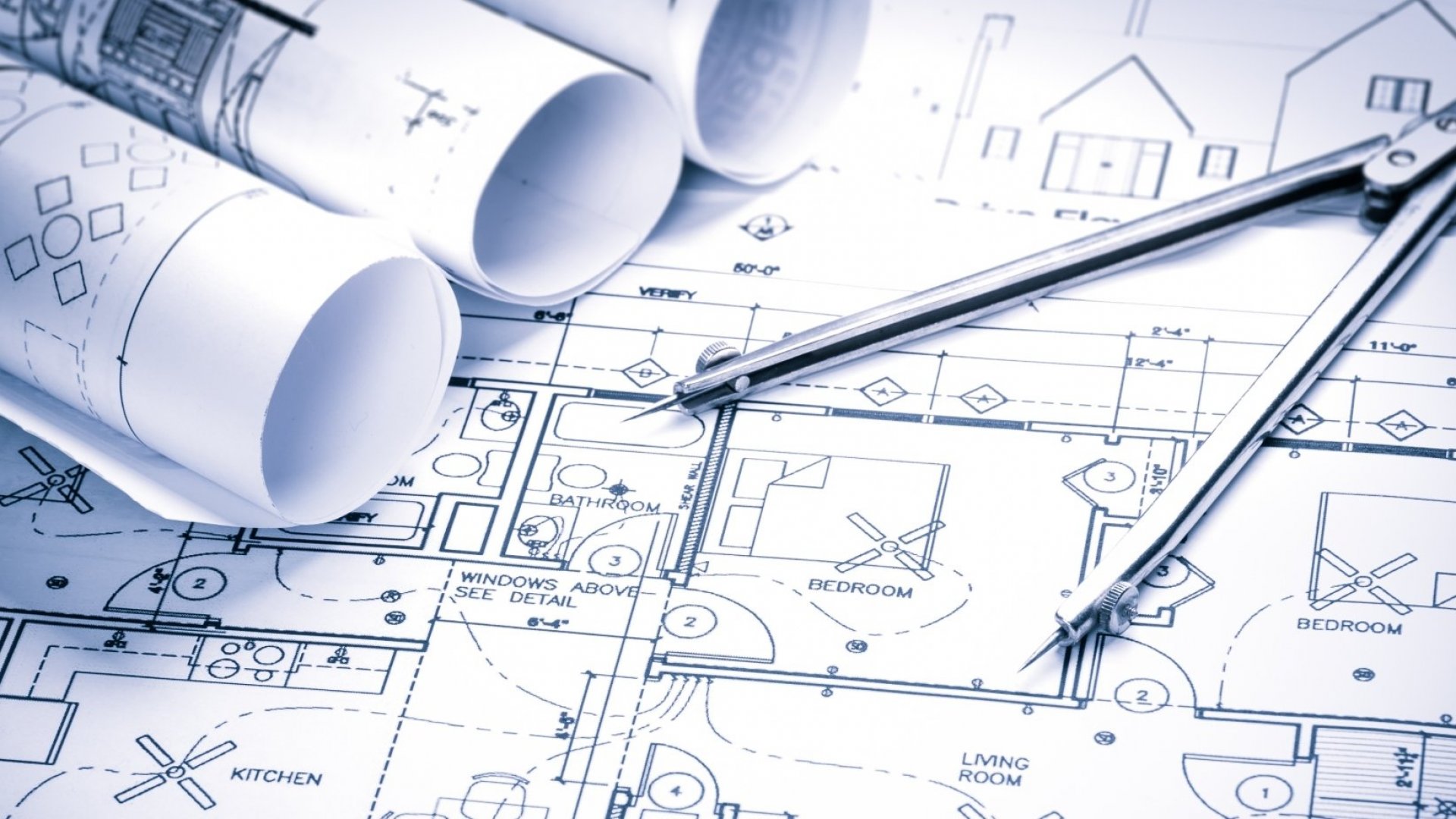
Architectural engineering is a broad field, and professionals in this area may specialize in different aspects such as structural engineering, building systems engineering, or environmental engineering. The goal is to create buildings that are not only visually appealing but also functional, sustainable, and resilient.

The planning phase sets the foundation for the entire architectural engineering process. It establishes a clear vision for the project, addresses potential challenges, and provides a roadmap for subsequent design, construction, and operation phases.
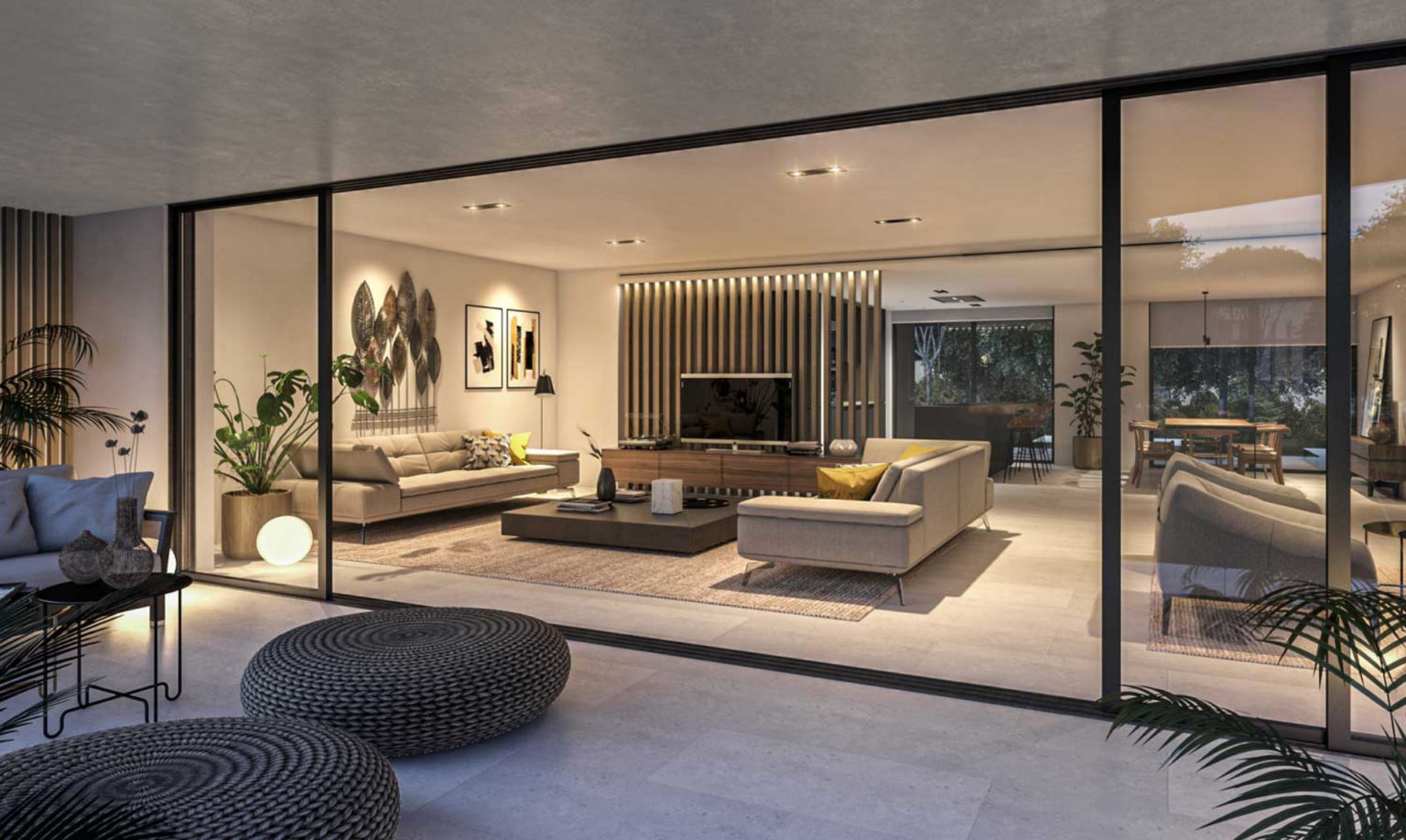

Interior design involves the planning and execution of the layout, furnishings, and decorations of a space to create a visually appealing and functional environment. This can include considerations such as color schemes, furniture selection, lighting, spatial arrangements, and overall aesthetic design.
Electrical design for a new house involves planning and specifying the electrical systems to ensure a safe and functional distribution of power throughout the home. Here are some key aspects of electrical design for a new house:
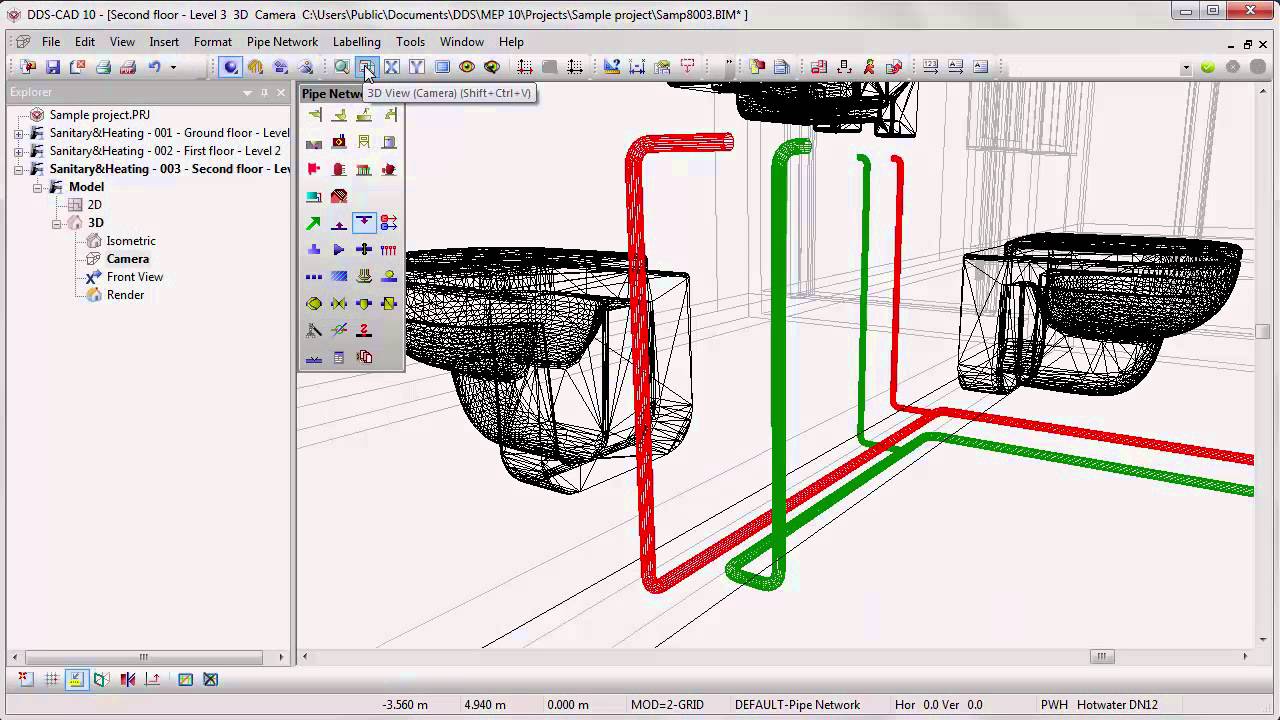
Plumbing design for a building involves planning and specifying the layout and installation of plumbing systems to ensure the proper distribution of water, drainage, and gas. Here are some key aspects of plumbing design:

Construction is a broad field that involves the planning, design, and execution of building projects. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including the construction of residential, commercial, and infrastructure projects. Here are some key aspects of construction:

Soil testing is a crucial process in various fields, including agriculture, civil engineering, environmental science, and construction. The primary purpose of soil testing is to analyze the physical and chemical properties of the soil to make informed decisions related to land use, crop management, construction projects, and environmental assessments. Here are key aspects of soil testing:

Estimating is a crucial aspect of civil engineering, particularly in the planning and execution of construction projects. Cost estimation involves predicting the expenses associated with a construction project, from the initial planning stages through completion. Accurate and detailed cost estimates are essential for budgeting, project financing, and decision-making. Here are key aspects of cost estimation in civil engineering:

It seems like your question is a bit broad, and I'd be happy to help if you provide more details or clarify your inquiry. However, if you're asking about building development in a general sense, here are some key points to consider:
Remember that each building development project is unique, and the specific steps and considerations may vary based on the type of development (residential, commercial, industrial) and the location. If you have a specific aspect you'd like more information on, please provide more details.
House No# 37, Meyapara, Ranibazar, Tiles Potti, Ghoramara, Rajshahi.